Linkage Between Cardiovascular Dynamics And Cycle Length Of Csb
Regarding the CL of CSB, Wedewardt et al. reported that, even among patients with similar AHI, the CL was longer in those with severe HF . Javed et al. demonstrated in the SERVE-HF substudy analysis that cardiovascular mortality and rate of hospitalization due to exacerbation of HF were higher in patients with HFrEF and longer CSB, and that the median CL in these patients was 64.5 and 62.1 s, respectively . Both reports showed a correlation between decreased cardiac output and increased CL of CSB.
In addition, Giannoni et al. showed that the lung-to-finger circulation time was the only independent predictive indicator of CL of CSB . Spiesshoefer et al. reported that a significant improvement in the left atrial pressure and circulatory delay, as well as a significant reduction in the ventilation length during central sleep hypopnea, was observed within 5 days after MitraClip implantation .
These reports also suggest that the CL of CSB reflects increased left atrial pressure and circulatory delay.
In the present study, which predominantly included patients with HFpEF, the CL was significantly increased during exacerbation of CHF even in the same patient. When we compared the CL between the CHF-stable and control groups, the CL in the CHF-stable group was significantly longer. Furthermore, patients with a short CL did not develop HF, despite a high CSB%. The optimal cut-off point that could predict the onset of HF was 68.9 s.
Cheyne Stokes Breathing And Other Abnormal Respiration
Overview
Cheyne Stokes breathing is a type of abnormal breathing. Its characterized by a gradual increase in breathing, and then a decrease. This pattern is followed by a period of apnea where breathing temporarily stops. The cycle then repeats itself.
Normal breathing, the process of moving air in and out of the lungs 12 to 20 times per minute, is something most people seldom think about. However, abnormal breathing like Cheyne Stokes is serious and may be frightening.
Central Sleep Apnea Symptoms
The main symptom of CSA is pauses in breathing. It usually doesnt cause snoring, the way obstructive sleep apnea does.
Symptoms also include:
- Being very tired during the day
- Waking up often during the night
- Having headaches in the early morning
- Trouble concentrating
- Not being able to exercise as much as usual
Don’t Miss: Sleep Number Bed Folsom Ca
Relationship Between Central Sleep Apnea And Cheynestokes Respiration
- Irena FlintaCorrespondenceCorresponding author at: 4th Military Hospital, Department of Cardiology ul. Weigla 5, 50-981 Wrocaw, Poland. Fax: +261 660 250.Department of Cardiology, 4th Military Hospital, Wrocaw, PolandDepartment of Physiology, Medical University, Wrocaw, Poland
- Department of Cardiology, 4th Military Hospital, Wrocaw, PolandClinic of Cardiac Diseases, Department of Heart Diseases, Medical University, Wrocaw, Poland
- Central sleep apnea common comorbidity in patient with heart failure
- CheyneStokes Respiration is the main manifestation of CSA in patients with HF.
- Substantial overlap between CSA and CSR in patient with HF
- CSA/CSR negative impact on prognosis and their importance for therapy in HF
- The potential compensatory role of CSR in HF hypothesis to further investigation
Viapproach In Selected Clinical Syndromes
The heterogeneity of central sleep apnea mandates an individualized treatment approach. Several factors have to be consideredfor proper management of each patient:
It is imperative to optimize treatment of the underlying condition such as CHF Follow up polysomnography is needed toconfirm improvement in the severity of apnea.
A trial of nasal CPAP is warranted as a starting point. There is good evidence that many patients may respond topositive pressure therapy. The optimal pressure settings have to be determined by a lab observed titrationpolysomnography.
The use of Bi-level-PAP in a pressure support mode is likely to aggravate the severity of central apnea. Adding abackup rate may be beneficial but should not be used for the treatment of CSA in HFrEF, given the potential for potential foradverse cardiac consequences from the constant inspiratory pressure in patients in whom right ventricle ispreload-dependent.58
Supplemental O2 may be beneficial in patients with CSA, particularly in patients with CHF-CSB.
The use of pharmacologic agents, remain very modest. Confirmation with efficacy with polysomnography is essential.Likewise, administration of this drug requires meticulous attention to serum levels.
Recommended Reading: Sleep Number I8 Vs I10 Reviews
Diagnosis Of Central Sleep Apnea
-
Clinical evaluation
-
Often polysomnography
Diagnosis of central sleep apnea is suspected on the basis of history and is confirmed by polysomnography Testing Almost half of all people in the US report sleep-related problems. Disordered sleep can cause emotional disturbance, memory difficulty, poor motor skills, decreased work efficiency, and increased… read more . However, testing may not be necessary if there are no symptoms instead, aggressive management of medical disorders that can cause sleep apnea Heart failure is a syndrome of ventricular dysfunction. Left ventricular failure causes shortness of breath and fatigue, and right ventricular failure causes peripheral and abdominal fluid… read more ) is tried first.
To diagnose central nervous system causes of central sleep apnea, brain or brain stem imaging may be indicated.
Intensive Heart Failure Treatment
Although it would seem prudent to ensure that patients with Cheyne-Stokes respiration are on optimal medical treatment for congestive heart failure, and as a result the severity of Cheyne-Stokes respiration would diminish, there are only limited supportive data. In patients with congestive heart failure a raised PCWP is associated with greater mortality. Moreover, intensive medical treatment can reduce both PCWP and mortality in a subset of patients with severe congestive heart failure patients so, as patients with Cheyne-Stokes respiration have raised PCWP, one would expect the Cheyne-Stokes respiration in a subset of patients to diminish in severity with intensive medical therapy. Limited evidence in support is provided by a single small short term non-randomised study in which a 50% reduction in the severity of Cheyne-Stokes respiration was observed with captopril over a four week period. Similar case series have reported reductions in Cheyne-Stokes respiration following intensive medical treatment,, cardiac valve surgery, and cardiac transplantation,,but conversion of Cheyne-Stokes respiration to obstructive sleep apnoea has also been reported following cardiac transplantation.
Recommended Reading: Reviews Of Eight Sleep Pod
Which Individuals Are At Greatest Risk Of Developing Central Sleep Apnea Syndrome
Risk Factors for CSA include:
-
Congestive Heart failure: 25-40 percent of patients with heart failure develop CSA/CSR.
-
Ascent to high altitude
-
Stroke patients: 10-28 percent of stroke patients have been reported to have CSA.
-
Narcotic use: 30 percent of opioid users develop CSA.
-
Age: CSA is more prevalent in older individuals.
-
Gender: Male hormones elevate the apneic threshold closer to eupneic levels and make males are more susceptible than females to developing CSA. In the general population, womens relative chance of developing CSA is 0.04 .
-
Other medical conditions, including Arnold Chiari malformation, hypothyroidism, acromegaly, renal failure, myopathies, neurodegenerative disorders, brainstem disorders, and atrial fibrillation in CHF
Supplemental Oxygen And Co2
Several studies have demonstrated a salutary effect of supplemental O2 in patients with central apnea associated withheart failure.55Physiologically, supplemental oxygen may alleviate central apneaby mitigating the magnitude of hypoxemia and hence dampening the magnitude of post-apneic ventilatory overshoot. In addition,isocapnic hyperoxia has been shown to stimulate ventilation in a dose-dependent manner.56 The most likely explanation is increased cerebral PCO2 by the displacement of carbon dioxidefrom hemoglobin by the increased oxygen level . The American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommends nocturnaloxygen as a standard treatment for central apnea related to heart failure.46
Supplemental CO2 abolishes central apnea in patients with central sleep apnea. The mechanism of action is by raising PCO2above the apneic threshold. However, this therapy is not practical given the need for a closed circuit to deliver supplementalCO2.
You May Like: Sleep Number Bed Gap In Middle
What Is Cheyne Stokes Breathing
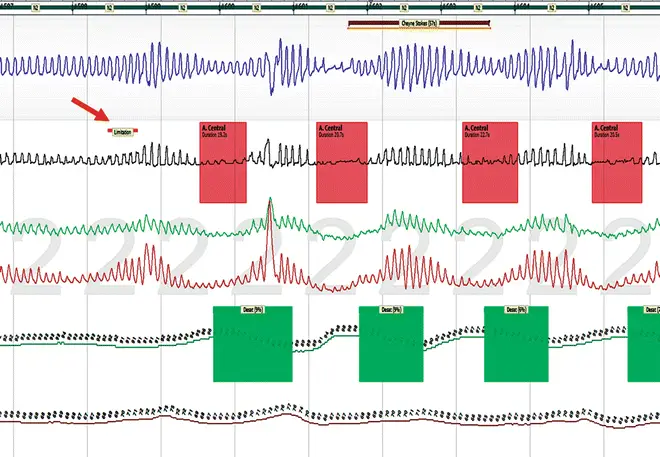
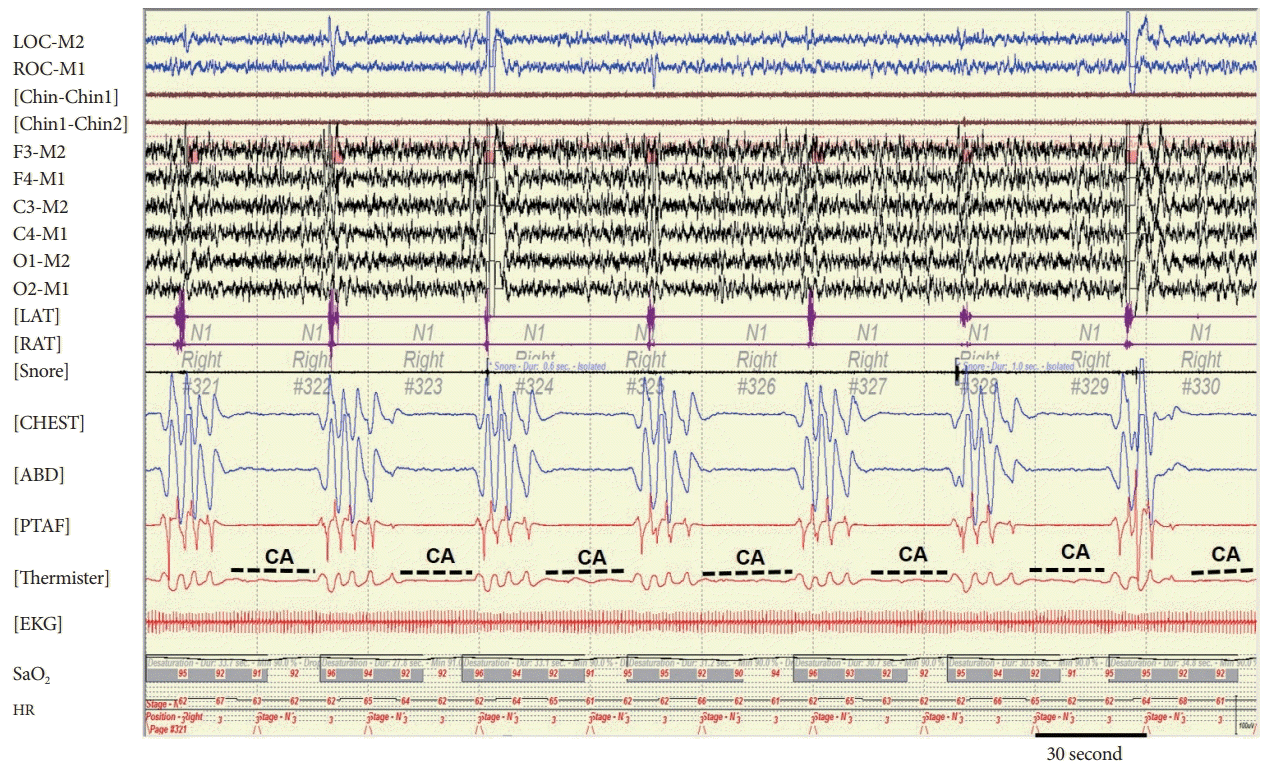
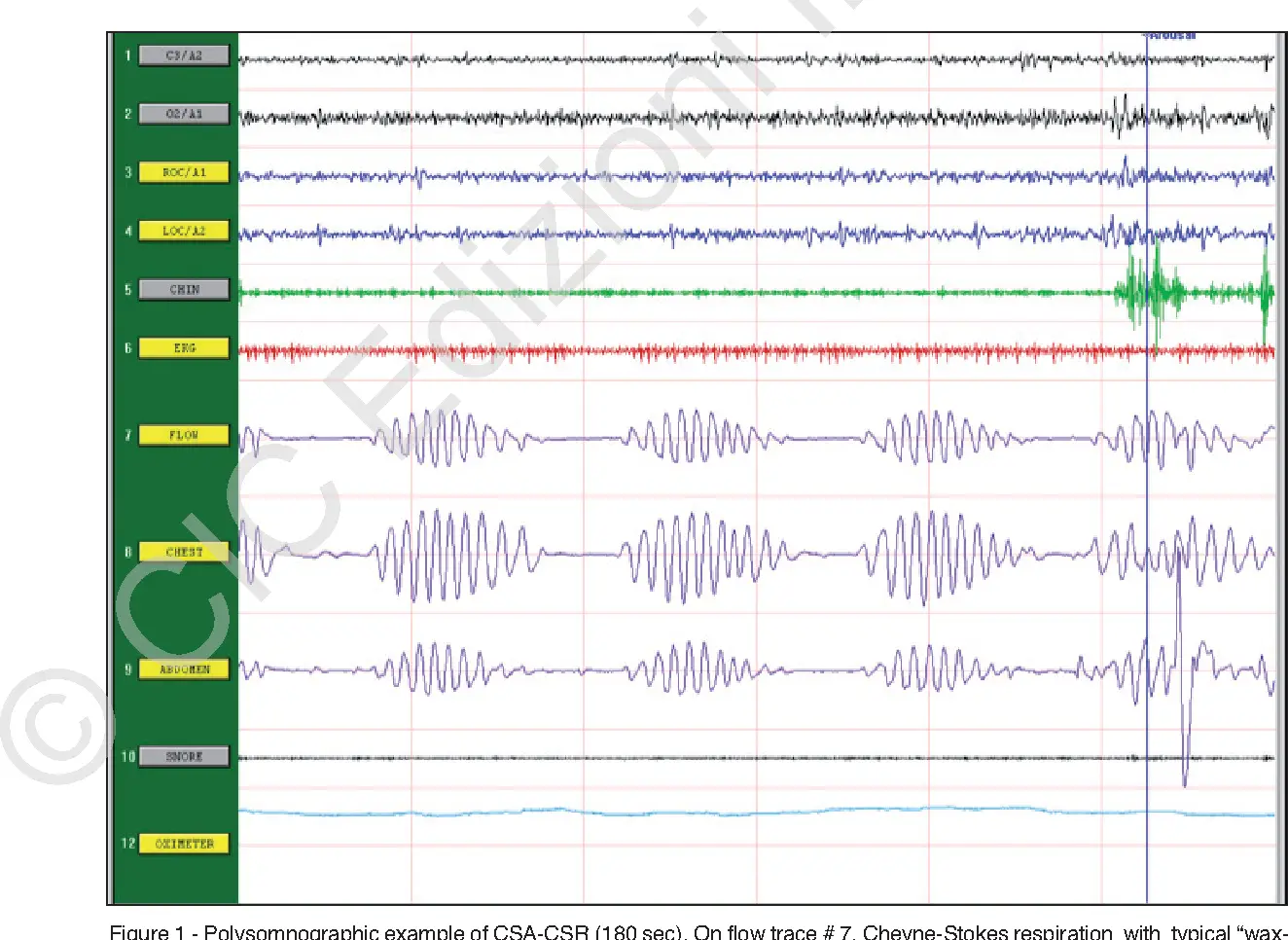
CSB-CSA is characterized by classic a crescendo-decrescendo pattern that typically occurs with a periodicity of 45 second or greater cycles . The ICSD-3 specifies that at least 10 central apneas and hypopneas per hour of sleep should occur, accompanied by arousals and derangement of sleep structure. The arousals occur at the peak of the hyperpnea phase. Patients usually have predisposing factors such as heart failure, stroke, or renal failure, as well as a lower resting PaCO2 than normal. See the following:
-
Renal failure
When Does It Most Likely Occur
According to research, Cheyne Strokes breathing can happen while youre awake, but is more common during sleep. It may happen more during non-rapid eye movement sleep than rapid eye movement sleep.
When Cheyne Stokes occurs during sleep, its considered a form of central sleep apnea with an extended period of fast breathing . Central sleep apnea causes you to stop breathing briefly and increases the levels of carbon dioxide in your body.
Cheyne Stokes is usually related to heart failure or stroke. It may also be caused by:
- brain tumors
- increased intercranial pressure
- chronic pulmonary edema
People who are dying often experience Cheyne Stokes breathing. This is a natural effect of the bodys attempt to compensate for changing carbon dioxide levels. While it may be distressing to those who witness it, theres no evidence Cheyne Stokes is stressful for the person experiencing it.
Don’t Miss: Best Sleeping Mattress On The Market
What Are The Clinical Consequences Of Viewing Csacsr As A Compensatory Mechanism For Advanced Hf
The first is to appreciate that the beneficial consequences of CSACSR mirror the effects of upper airway, pulmonary and cardiac effects of CPAP, although periodically rather than continuously. The second is to use the periodicity of cardiac autonomic control , controlled by the powerful periodic respiratory drive, as a useful surrogate marker of underlying CSACSR when ventilation is stabilised by treatments directed specifically at CSACSR, such as adaptive servo-controlled ventilation. Finally, treatments that replace periodic central apnoeas with continuous stimulation of ventilation , such as theophylline, inhaled carbon dioxide or dead space, may lead to detrimental respiratory muscle fatigue.
Results In The Context Of The Literature
Four RCTs were not entered in the quantitative network meta-analysis because they did not report sufficient outcome data on LVEF. The conclusions from these trials did not alter the findings of the network meta-analysis .
There remains a need for large RCTs including patients with sufficient adherence to PPV, and the upcoming results of the ongoing ADVENT-HF trial may provide further insight into the effects of ASV on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with heart failure and sleep-disordered breathing .
Read Also: Are You Put To Sleep For Lasik
Central Sleep Apnea Risk Factors
Anyone could have any of the types of sleep apnea. Central sleep apnea is more common among older people, especially those over 65. They may have health conditions or sleep patterns that make them more likely to get CSA.
Men are at higher risk of both central and obstructive sleep apnea.
Conditions that may be linked to central sleep apnea include:
- Avoid alcohol and sleeping pills, which make your airway more likely to collapse while you sleep.
- Sleep on your side instead of on your back.
- Use nasal sprays or breathing strips to keep air flowing if you have sinus problems or nasal congestion.
- Get plenty of sleep.
Continuous positive airway pressure can help people with all kinds of sleep apnea, especially CSA caused by heart failure.
A CPAP machine forces a constant stream of air into your nose and mouth through a mask you wear while you sleep. The air pressure is just enough to keep your upper airway tissues from collapsing and blocking your breathing. If you have trouble with CPAP, you might try similar devices called adaptive servo-ventilation and bilevel positive airway pressure .
A device called the Remede System can help with moderate to severe central sleep apnea. Your doctor implants a small machine under the skin in your upper chest. It helps trigger the nerve that moves your diaphragm when you breathe. It also monitors your respiratory signals while you sleep and helps restore regular breathing patterns.
Continued
Search Strategy And Trial Identification
PubMed/Medline, Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were searched up to December 2017 using the following search terms: AND AND AND random*. Full texts and/or abstracts were screened to identify eligible trials. Trial registries and bibliographies of all eligible RCTs were additionally screened. Two authors independently performed the literature search.
Also Check: Best Mattress For Sleeping On Your Side
What Is Cheyne Stokes Respiration
Cheyne Stokes respiration, also known as agonal respiration, is an unique breathing pattern usually characterized by three phases:
- a crescendo phase in which tidal volume increases gradually with each breath from hypopnea to hyperpnea,
- a decrescendo phase from hyperpnea to hypopnea,
- a central apnea phase
In this video you’ll see a live demonstration of agonal respiration:
Barra Lateral Del Artculo
Ninguna publicación, nacional o extranjera, podrá reproducir ni traducir sus artículos ni sus resúmenes sin previa autorización escrita del editor sin embargo los usuarios pueden descargar la información contenida en ella, pero deben darle atribución o reconocimiento de propiedad intelectual, deben usarlo tal como está, sin derivación alguna.
You May Like: Sit N Sleep Customer Service
Maintaining A State Of Respiratory Alkalosis
Although Dr. Naughton writes about debatable beneficial effects of hypocapnia on the myocardium, he does not mention that hypocapnia is a profound vasoconstrictor of both cerebral and coronary vessels. It has been shown that hyperventilation can be a specific test for diagnosing coronary artery spasm.17 In the context of HCSB, concomitant hypocapnia and hypoxemia could decrease myocardial oxygen delivery, adversely affecting the failing heart. Furthermore, hypocapnia and alkalemia are known to be arrhythmogenic and arrhythmias are common in patients with HFrEF, especially in those with CSA-HCSB.1820 In two studies of patients with HFrEF and CSA-HCSB, overnight Holter monitoring revealed that low arterial PCO220 and alkalemia19 were associated with nocturnal ventricular tachycardia. These data strongly support the possibility that alkalemia is involved in the demise of patients from what is aptly described as sudden death in the cardiology literature.
Treatment Of Central Sleep Apnea
-
Supportive care
Primary treatment of central sleep apnea is optimal management of underlying disorders and avoidance of opioids, alcohol, and other sedatives. Secondary treatment of symptomatic patients can be a trial of supplemental oxygen or, in patients with hypercapnic CSA who have symptoms despite other treatments, noninvasive continuous or bilevel positive airway pressure.
Recently, a transvenous phrenic nerve stimulation system has become available. The system is programmed to produce a rhythmic breathing pattern that stabilizes tidal volume, airflow, and oxygenation, entraining breathing during sleep and potentially altering disease progression is a heterogeneous group of conditions characterized by changes in ventilatory drive without airway obstruction. Most of these conditions cause asymptomatic changes… read more ).
Read Also: The Edge Of Sleep Podcast
Quality And Bias Assessment
Quality of the included trials was independently assessed by two authors using the Cochrane Collaborations tool for assessing risk of bias. Funnel plots were used to visualize potential publication and other bias. The quality of the estimated treatment effect in the network meta-analysis was rated using the approach of the GRADE working group considering the extent of the contribution of direct and indirect evidence.,
Effect Size In The Context Of Long
The minimal clinically important difference in LVEF or the cutoff for responders to therapy is not well defined but has been estimated to be about 5%. The interobserver variability of LVEF estimation by echocardiography and application of the modified biplane Simpson rule to quantify LVEF is of similar size. Despite small effects in absolute percent change in LVEF in response to PPV in CSA/CSR and heart failure, an absolute improvement of 5% in a patient with a LVEF of 30% translates into a relative improvement of 17%. This effect size may lift the patient from the category of severely reduced LVEF to a more moderately reduced category, which holds a better prognosis. The effect of treating CSA/CSR is comparable to the effect size of pharmacotherapy or other interventions on LVEF in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, for example, beta-blockers ,, cardiac resynchronization therapy , or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors .
Recommended Reading: New Jersey Sleep Apnea Solutions
Definitions Of Csb% Detected By The Cpap Device
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommends scoring a respiratory event as CSB if both of the following criteria are met:
-
a. There are episodes of at least three consecutive central apneas and/or central hypopneas separated by a crescendo and decrescendo change in the breathing amplitude, with a cycle length of at least 40 s .
-
b. There are five or more central apneas and/or central hypopneas per hour associated with a crescendo/decrescendo breathing pattern recorded over a minimum of 2 h of monitoring.
According to the algorithm of the CPAP device, the device detects periodic breathing that meets only criterion a. Thus, in this study, we defined CSB% as the percentage of time exhibiting periodic breathing to the duration of the CPAP device use as recorded in the CPAP data.
Central Sleep Apnea Causes And Types
There are several types of central sleep apnea, each with a different cause.
- Cheyne-Stokes breathing. This is when your breathing speeds up, slows down, stops, and then starts again. Each of these cycles can last 30 seconds to 2 minutes. Cheyne-Stokes breathing is common in people whove had heart failure or a stroke. It happens in about half of central sleep apnea cases.
- Narcotic-induced central sleep apnea.Opioid medications like morphine, oxycodone, and codeine can affect your breathing patterns.
- High-altitude periodic breathing. Many people have trouble breathing when they go up to a high elevation, usually 2,500 meters or more.
- Treatment-emergent apnea. About 5% to 15% of people who have positive airway pressure treatment for obstructive sleep apnea get CSA.
- Medical condition-induced apnea. Health problems like heart failure, Parkinsons disease, stroke, and kidney failure can cause CSA.
- Idiopathic central sleep apnea. This is when theres no clear cause.
A related condition named congenital central hypoventilation syndrome is linked to a certain gene. It affects about one in 200,000 children around the world.
Continued
You May Like: Sleep Number Store Greensboro Nc